Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)

Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) is a condition that causes an abnormally fast heart rate when standing up from a lying or sitting position. This can lead to symptoms such as lightheadedness, dizziness, and fainting.
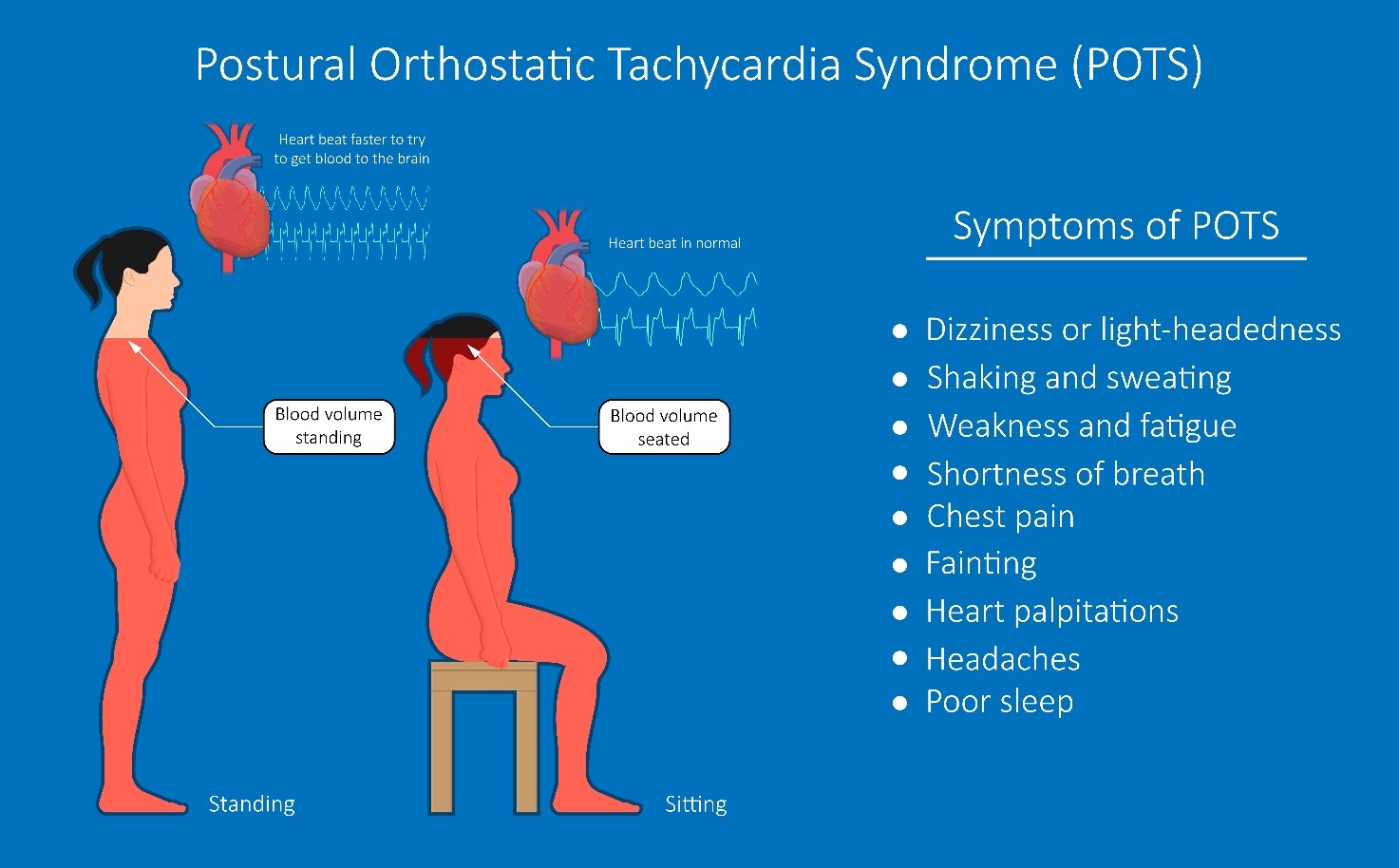
Symptoms of POTS
- Lightheadedness or dizziness upon standing
- Rapid heart rate (over 120 beats per minute) within 10 minutes of standing
- Fainting
- Fatigue
- Brain fog
- Difficulty concentrating
- Headaches
- Blurred vision
- Nausea
Causes of POTS
The exact cause of POTS is unknown, but it is thought to be related to a problem with the autonomic nervous system, which controls the body’s automatic functions such as heart rate and blood pressure.
Some of the factors that may contribute to POTS include:
- Dehydration
- Hormonal changes
- Medications
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or lupus
Diagnostic Criteria for POTS
The diagnosis of POTS is based on the following criteria:
- Symptoms of POTS, such as lightheadedness or dizziness upon standing
- A heart rate that increases by at least 30 beats per minute within 10 minutes of standing
- No other medical condition that could explain the symptoms
Impact of POTS: Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome
POTS can have a significant impact on daily life. Symptoms can make it difficult to participate in activities, such as school, work, and social events. People with POTS may also experience fatigue, dizziness, and fainting.
Psychological Effects
The psychological effects of POTS can be just as debilitating as the physical symptoms. People with POTS may experience anxiety, depression, and social isolation. They may also have difficulty concentrating and making decisions.
Long-Term Complications
If left untreated, POTS can lead to several long-term complications, including:
– Chronic fatigue
– Heart failure
– Stroke
– Kidney failure
Management and Treatment of POTS
The management of POTS involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and exercises. The goal of treatment is to improve symptoms, prevent complications, and enhance quality of life.
Treatment options for POTS can be categorized into the following:
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Medications
- Exercises and Techniques
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can help manage POTS symptoms and improve overall well-being. These include:
- Increasing fluid intake to at least 2-3 liters per day
- Consuming adequate salt intake, around 2-3 grams per day
- Wearing compression stockings to improve blood flow in the legs
- Elevating the legs above the heart level when sitting or lying down
- Avoiding prolonged standing or sitting
- Getting regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or biking
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals to avoid large fluctuations in blood sugar levels
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises
Exercises and Techniques, Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
Specific exercises and techniques can help improve symptoms of POTS. These include:
- Tilt-table training: This involves gradually increasing the angle of a tilt table while monitoring symptoms. It helps the body adapt to changes in posture.
- Graded exercise therapy: This involves gradually increasing the intensity and duration of exercise to improve cardiovascular fitness.
- Deep breathing exercises: These exercises help regulate heart rate and blood pressure.
- Valsalva maneuver: This involves exhaling against a closed glottis, which can help increase blood pressure.